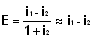International Fisher Effect - IFE
An economic theory that states that an expected change in the current exchange rate between any two currencies is approximately equivalent to the difference between the two countries' nominal interest rates for that time.
Calculated as:
Where:
"E" represents the % change in the exchange rate
"i1" represents country A's interest rate
"i2" represents country B's interest rate
|||For example, if country A's interest rate is 10% and country B's interest rate is 5%, country B's currency should appreciate roughly 5% compared to country A's currency.
The rational for the IFE is that a country with a higher interest rate will also tend to have a higher inflation rate. This increased amount of inflation should cause the currency in the country with the high interest rate to depreciate against a country with lower interest rates.
热门专栏
热门词条
应收账款
区域货币
区间估计
金融危机
资本成本
CPI(Consumer Price Index)
汇率
资产
经济
美元
单向定单
租赁期
外汇通
外汇佣金
服务
SME
ISO
认可
增量成本
什一税
CFO
MIT
加工
MG金融集团
销售
股价反弹
抽签偿还
股利收入
技术
空头陷阱
资本
REF
市场
中国股市
中小企业
备付金率
美国
两会
价格
吊空
指数
股灾
葡萄牙币
调至市价
pt
清算
电子汇兑
税粮
下降三角形
外汇
FDI
投资
Writer
银行
阴烛
管理
MACD
企业
width
黄金
冲账
短期同业拆借
Theta
peg
货币
外汇交易法
金融中介理论
艾略特波段理论的含义
消费发展战略
产品
巴塞尔资本协议
计期汇票
贴现现金流
联系汇率制度
拔档
美国贝勒大学
汇差清算率
延期付款汇票
短期国际商业贷款
Exposure
集中竞价
标准普尔(S&P)
金融
不完全竞争市场理论 (金融)
公司
正利差
分期付款汇票
软通货
出口物价指数
指标
选择权买方
资金
单位
百分比回撤
无记名汇票最低报价戴维·凯特标准·普尔 500指数抵押品持平德国工业产值德国消费者物价指数成本协同效益
非农就业人口
股票
交易
道琼斯公用事业平均指数
持平
指示汇票
产品竞争力
财务指标 盈利能力比率
外汇实盘交易方式
德国伊弗研究所景气调查